AQS框架之ReentrantReadWriteLock实现类
现在就只剩下一个常量我们没有用到了:PROPAGATE,这个常量在ReentrantReadWirteLock类中有用到,既然是读写锁,那么其特性有哪些呢?
- 当读锁被占有时,后续依然可以获取读锁
- 当读锁被占有时,写锁不可被获取
- 当写锁被占有时,读写锁都不可被获取
- 由类名可知,锁可重入
status这个域是用来记录重入锁的次数的,非0即为锁被获取,那么就有几个问题会被抛出
- 如何用一个值既要记录读锁的重入数,又要记录写锁的重入数?
- 读锁是可以被多个线程共同持有的,每个线程又有自己的重入数,如何记录?
ReentrantReadWirteLock的类图如下
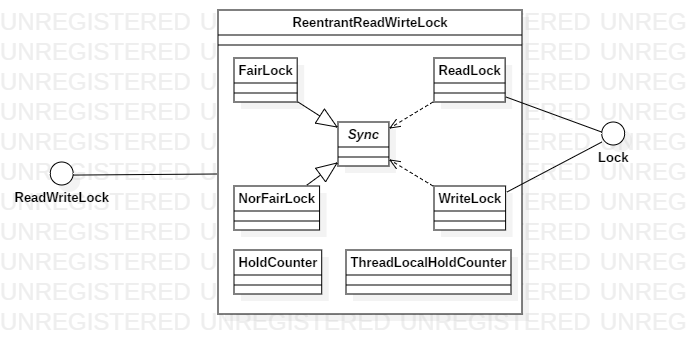
可以看到,在ReentrantReadWirteLock类中多出了两个内部类,其源码如下
static final class HoldCounter {
int count = 0;
final long tid = getThreadId(Thread.currentThread());
}
static final class ThreadLocalHoldCounter
extends ThreadLocal<HoldCounter> {
public HoldCounter initialValue() {
return new HoldCounter();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
其中,HoldCounter类用来保存本线程的重入数,而每个线程使用ThreadLocal来保存HoldCounter,这里引出ReentrantReadWirteLock类中的几个私有域
| 域名 | 类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| readHolds | ThreadLocalHoldCounter | 当前线程读锁的重入数 |
| cachedHoldCounter | HoldCounter | 最后一个成功申请读锁的重入数 |
| firstReader | Thread | 第一个获取读锁的线程 |
| firstReaderHoldCount | int | 第一个获取读锁的线程的重入数 |
每个线程自己的读锁的重入数保存在readHolds中,接下来我们来看下读锁的申请锁源码
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
这两段代码就已经规定好了申请读锁的大框架——尝试申请锁失败,进入循环阻塞
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
//有且仅有独占线程不是当前线程时会返回-1,即失败
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&
r < MAX_COUNT &&
//尝试获取读锁
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
//读锁没有被获取过
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
//读锁被重入获取
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
在尝试获取读锁的那段代码就回答了我们的第一个问题,ReentrantReadWirteLock将status值分为了两部分,前16位保存读锁的总重入数,后16位保存写锁的重入数
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
//--(1)--
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
//--(2)--传播
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
看到上述doAcquireShared方法是不是很眼熟,这代码结构明显就和doAcquire一模一样啊。没错,但是还是有一些不同
- 添加节点时添加的是Node.SHARED模式而不是独占模式(Node.EXCLUSIVE)
这里引入在Node节点中的两个常量
/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
/** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
- 当申请成功时,多了一行setHeadAndPropagate方法
我们设想这么一个场景:当前写锁被占有,然后来了几个申请读锁的线程,这几个线程被阻塞排队,而后写锁被释放,第一个申请读锁的线程获取到锁。这个时候,后续的读锁也应该获取到读锁。这种情况我们称其为读锁传播,也就是setHeadAndPropagate做的事情
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
setHead(node);
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
//后继节点需要唤醒
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
//释放后继节点
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
//后继节点不需要唤醒
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
在doReleaseShared这就和我们在最开始提到的PROPAGATE相关联了
